Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Takano, Masahide; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Soichi; Tanaka, Kosuke
Current Location of Fuel Debris Chemistry, 178 Pages, 2023/11
Considerable efforts have been devoted to the decommissioning of the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) and now the retrieval of fuel debris is being proceeded on a trial basis. It can be said that the succession of science and technology related to debris, that is, human resource development, is important and indispensable. For that reason, we thought that a specific textbook on decommissioning is necessary. Regarding the 1F fuel debris, we still do not know enough, and it would be difficult to describe the details. However, 12 years have passed since the accident, and we have come to understand the situation of 1F to a certain extent. At this stage, it is essential for future development to organize the current situation by combining examples of past severe accidents. Therefore, we presented in this book the current state of fuel debris chemistry research from the perspectives of solid chemistry, solution chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiochemistry, and radiation chemistry.
Hirade, Tetsuya
AIP Conference Proceedings 2182, p.030007_1 - 030007_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:84.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)There are many new application of room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) for many different fields. One of them is reprocessing spent nuclear fuels and then research of irradiation effects on RTILs are very important. The positron annihilation techniques are very strong tool to investigate fast reactions of excess electrons. Positron annihilation age-momentum correlation (AMOC) experiment was applied to deepen understanding the phenomena occurred at very young positron ages. We clarified that Ps bubble formation in RTILs was very slow and, finally, oscillation of Ps bubble was observed just after the Ps formation at near melting temperatures. These results can indicate that Ps formation occurred in very short time in RTILs. The phenomena observed by Ps just in RTILs will be discussed.
Kumagai, Yuta
Radioisotopes, 66(11), p.537 - 541, 2017/11
Radiation effects on the mixtures of inorganic oxides and water have been investigated for understanding radiation chemistry in solid-liquid systems. A number of studies revealed that energy deposition on solid phase stimulates reactions at the interface. This energy/charge transfer has been demonstrated by experiments to affect early stage of the radiation-induced reaction. However, the interfacial reactions subsequent to the energy/charge transfer require further studies. Here, we will see gaps between the basic understanding on the early stage and radiation effects in solid-liquid systems connected to applications, taking zeolite/water and uranium oxide/water interfaces for examples. Understanding of the interfacial reactions subsequent to the energy/charge transfer would bridge the gaps and enable to predict the radiation effects in applications.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Radioisotopes, 66(11), p.587 - 593, 2017/11
Positron, anti-particle of electron, annihilates with the lifetime of 100ps to several ns in condensed matter. The energy of the mass of both particles emits as two  -rays. The annihilation rate of energy of
-rays. The annihilation rate of energy of  -rays indicate information just before the annihilation. Positrons have some possibility of reaction with excess electrons to form Positronium (Ps). Ps formation occur within ~ps, therefore Ps formation can be a probe of very fast reactions. Moreover, long lived triplet Ps can have reaction with reactive species until the lifetime of ~ns. Here, methods of positron annihilation research for radiation chemistry and some researches done by positron annihilation methods are introduced.
-rays indicate information just before the annihilation. Positrons have some possibility of reaction with excess electrons to form Positronium (Ps). Ps formation occur within ~ps, therefore Ps formation can be a probe of very fast reactions. Moreover, long lived triplet Ps can have reaction with reactive species until the lifetime of ~ns. Here, methods of positron annihilation research for radiation chemistry and some researches done by positron annihilation methods are introduced.
Yamashita, Shinichi*; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Maehashi, Yuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hata, Kuniki; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
RSC Advances (Internet), 5(33), p.25877 - 25886, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:38(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pulse radiolysis experiments were carried out to observe transient absorptions of reaction intermediates produced in N O
O and Ar-saturated aqueous solutions containing 0.9-900 mM NaBr. The most important species among the reaction intermediates are BrOH
and Ar-saturated aqueous solutions containing 0.9-900 mM NaBr. The most important species among the reaction intermediates are BrOH 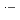 and Br
and Br
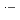 , which commonly have absorption peaks around 360 nm. The experimental results were compared with the results of simulation based on a spur diffusion model. Each of several complicated sequential radiation-induced chemical reactions was carefully considered, optimizing its rate constant within a range of reported values. All the experimental results were able to be universally reproduced by the simulation, assuming a reaction not yet reported, 2BrOH
, which commonly have absorption peaks around 360 nm. The experimental results were compared with the results of simulation based on a spur diffusion model. Each of several complicated sequential radiation-induced chemical reactions was carefully considered, optimizing its rate constant within a range of reported values. All the experimental results were able to be universally reproduced by the simulation, assuming a reaction not yet reported, 2BrOH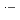
 Br
Br + 2OH
+ 2OH , with a rate constant of 3.8
, with a rate constant of 3.8  10
10 M
M s
s , which is significant only within 10 micro-s for rather high bromide concentrations (
, which is significant only within 10 micro-s for rather high bromide concentrations ( 10 mM). Primary
10 mM). Primary 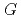 values, which are yields after sufficient diffusion from the spur to the perimeter region during 100 ns, of major water decomposition products, as well as of the reaction intermediates, were calculated for N
values, which are yields after sufficient diffusion from the spur to the perimeter region during 100 ns, of major water decomposition products, as well as of the reaction intermediates, were calculated for N O
O and Ar-saturated conditions as a function of NaBr concentration.
and Ar-saturated conditions as a function of NaBr concentration.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 76(2), p.84 - 89, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.51(Chemistry, Physical)There are many connections between radiation and positronium chemistry. The Spur Reaction model proposed by Mogensen needs much radiation chemistry knowledge. On the other hand, the Spur Reaction model could give new ideas to radiation chemists. Positronium formation reaction is very fast and hence there is a good relationship between reactions observed by a pulse radiolysis measurement and positronium formation, which was shown by Dupratre et al. Enhancement of positronium formation at low temperatures was successfully explained by the reaction of trapped electrons and positrons. The trapped electrons have been studied well by radiation chemists. That knowledge was needed to propose a new idea to explain the positronium formation at low temperatures. And now, probably it is becoming possible to use the positronum formation reaction to study the trapped electrons. Positron methods will be able to be used for the radiation chemistry research.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Hoshasen Kagaku, (77), p.2 - 7, 2004/05
no abstracts in English
Working Group in the Advisory Committee of the Analytical Studies for Application of Charged Particl
JAERI-Review 2003-008, 42 Pages, 2003/03
The position in the research field of radiation application of "Theoretical Analysis Group for Radiation Application" which will be set up within fiscal 2003, and the relation between the research that this analytical group will advance in future and the analytical research made so far at JAERI Takasaki are summarized. First, the theoretical analysis group for radiation application extracts only the core element from the analysis of reactive process of charged particles in the materials and from the irradiation effect, and then constructs the simplified model. Second, the validity of the constructed model is verified by advancing the theoretical analysis based on the model, and the calculated result is fed back to the experiment, and then the verification is carried out. Finally, the general-purpose theorization will be conducted by generalizing and universalizing the obtained model concerning the specific system. The obtained outcomes will be applied to other systems, and, will consequently, contribute to the promotion of new technological development.
Hirade, Tetsuya
Hoshasen Kagaku, (75), p.46 - 51, 2003/03
Enhancement of positronium (Ps) formation at low temperatures has been observed in many materials since 1980's. There were some interpretations. However, none of them explained the phenomena successfully. In 1998, a new idea of the Ps formation was proposed and the expected phenomena were successfully observed. This new Ps formation process will be explained with those experimental results and the possibility of usage of Ps formation for radiation chemistry researches will be also discussed.
Koizumi, Hitoshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Ichikawa, Tsuneki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 179(4), p.530 - 535, 2001/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shoji
Earozoru Kenkyu, 16(2), p.145 - 146, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Yamaoka, Hitoshi*; Hase, Hirotomo*; Makuuchi, Keizo
JAERI-Conf 2000-001, p.331 - 0, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Tamada, Masao
Hoshasen Kagaku, (68), p.43 - 44, 1999/09
no abstracts in English
Arai, Taketoshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; Terai, Takayuki*; Ishino, Shiori*
ECN-R--98-005, p.113 - 124, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
 March 1996
March 1996JAERI-Review 96-017, 277 Pages, 1997/01
no abstracts in English
 -rays and heavy ions
-rays and heavy ions*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Namba, Hideki; *; *
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 132, p.633 - 638, 1997/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:46.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Tachimori, Shoichi; *
JAERI-Data/Code 96-030, 116 Pages, 1996/10
no abstracts in English
*; *; *; Namba, Hideki; ; Kojima, Takuji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 117, p.431 - 435, 1996/00
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:82.8(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Advanced Science Research Center
JAERI-Conf 95-020, 81 Pages, 1995/10
no abstracts in English